How to operate a drone is a question many ask, opening up a world of aerial photography, videography, and exploration. Understanding the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, is crucial for safe and successful flights. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, covering everything from basic controls to legal considerations, empowering you to take to the skies responsibly and confidently.
We’ll explore the essential steps involved in preparing for a flight, including thorough pre-flight inspections and understanding safety regulations. You’ll learn how to master drone controls, execute various flight maneuvers, and utilize advanced features such as waypoints and obstacle avoidance. Finally, we’ll address post-flight procedures and the importance of ongoing maintenance for optimal drone performance and longevity.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting various components, verifying system functionality, and assessing environmental conditions. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
Before each flight, a comprehensive inspection is essential. The following table Artikels key components and their acceptable and unacceptable conditions:
| Component | Inspection Item | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery | Charge Level | Above 80% capacity; no visible damage | Below 20% capacity; swelling; damage to casing |
| Propellers | Integrity | No cracks, bends, or chips; securely fastened | Cracks, bends, or chips; loose or damaged |
| GPS | Signal Strength | Strong signal, at least 8 satellites acquired | Weak signal; less than 5 satellites acquired; unable to acquire GPS lock |
| Camera (if applicable) | Lens and Gimbal | Lens clean and clear; gimbal moves smoothly | Lens dirty or scratched; gimbal jerky or unresponsive |
| Airframe | Structural Integrity | No visible damage or cracks; all components securely attached | Cracks, damage to arms or body; loose components |
Battery Levels, Propeller Condition, and GPS Signal
Checking battery levels ensures sufficient flight time and prevents unexpected power loss mid-flight. Inspecting propellers for damage prevents mid-flight failure. A strong GPS signal is essential for accurate positioning and safe autonomous flight modes like Return-to-Home.
Flight Delay or Cancellation Decision Flowchart
A clear decision-making process is essential for determining whether to proceed with a flight. The following flowchart Artikels the steps involved:
[Diagram would be inserted here. A textual description follows:]
Start -> Check Weather Conditions (Wind speed, precipitation, visibility) -> Acceptable? Yes -> Check Drone Status (Battery, GPS, Propellers) -> Acceptable? Yes -> Proceed with Flight -> No -> Delay or Cancel Flight -> End. If any condition is unacceptable, the process branches to “Delay or Cancel Flight.”
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respect the privacy of others and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Be aware of local laws and regulations governing drone operation.
- Fly responsibly and avoid endangering people or property.
- Always have a backup plan in case of technical issues.
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes is essential for safe and effective operation. This section covers the basics of drone control and the different flight modes available.
Drone Control Sticks
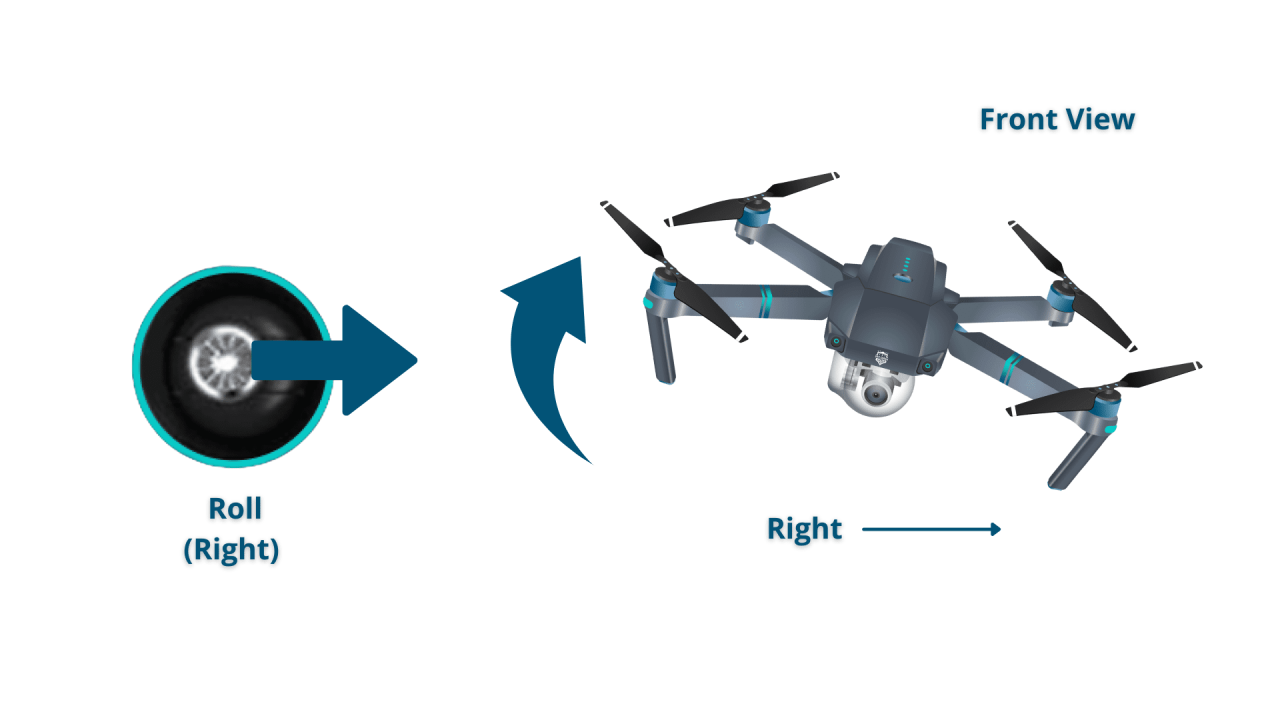
Most drone controllers use two joysticks. The left stick typically controls the drone’s altitude and horizontal movement. The right stick controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and pitch/roll (tilting).
[Illustrations of joystick movements and their effect on drone flight would be included here. A textual description is provided instead.] Left stick: Up = ascend, Down = descend, Forward = move forward, Backward = move backward. Right stick: Left = yaw left, Right = yaw right, Forward = pitch forward (nose down), Backward = pitch backward (nose up).
Flight Modes Comparison
| Flight Mode | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attitude Mode | Controls drone movement relative to its current orientation. | Highly maneuverable; good for close-range flight. | Can be less stable in windy conditions; requires more pilot skill. |
| GPS Mode | Maintains drone position using GPS signals. | Stable flight; good for long-range flights. | Less maneuverable; requires strong GPS signal. |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) Mode | Automatically returns the drone to its home point. | Safety feature; useful in case of signal loss. | May not be accurate in areas with weak GPS signal or obstacles. |
Compass and GPS Calibration
Regular calibration of the drone’s compass and GPS ensures accurate positioning and stable flight. The specific procedures vary depending on the drone model, but generally involve a series of movements guided by the drone’s software.
Maintaining Control and Stability in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions requires more skill and attention. It is important to adjust your control inputs smoothly and gradually, anticipating wind gusts and maintaining a stable flight path. Lowering your flight speed and keeping the drone at a lower altitude can also increase stability.
Taking Off, Landing, and Basic Maneuvers
This section covers the fundamental steps for taking off, landing, and performing basic maneuvers with your drone.
Safe and Controlled Takeoff Procedure
- Ensure the drone is fully charged and calibrated.
- Find a safe, open area away from obstacles and people.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Gently lift the drone using the control stick.
- Hover the drone at a low altitude before beginning your flight.
Smooth and Precise Landing Procedure
- Slowly descend the drone using the control stick.
- Maintain a steady descent rate to avoid a sudden impact.
- Once the drone is close to the ground, gently lower it to a complete stop.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
- Hovering: Maintaining a fixed position in the air.
- Ascending: Moving upwards.
- Descending: Moving downwards.
- Yawing: Rotating the drone left or right.
- Pitching: Tilting the drone forward or backward.
- Rolling: Tilting the drone left or right.
Practicing Basic Flight Patterns
Practicing basic flight patterns like squares, circles, and figure eights helps develop control and coordination. Start with slow, deliberate movements, gradually increasing speed and complexity as your skills improve.
Advanced Flight Techniques and Features
This section delves into more advanced flight techniques and features commonly found in modern drones.
Waypoints and Automated Flight Planning
Many drones offer waypoint functionality, allowing you to pre-program a flight path. This feature is useful for capturing aerial photography or videography, particularly for complex shots or repetitive maneuvers. Automated flight planning software can further simplify the process.
Obstacle Avoidance Systems
Modern drones often include obstacle avoidance systems using sensors to detect and avoid obstacles. These systems improve safety and allow for more autonomous flight in complex environments. However, it’s crucial to remember that these systems are not foolproof and should not be solely relied upon.
Drone Cameras and Image Stabilization
High-quality cameras and image stabilization are key features for aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings, such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO, is crucial for capturing professional-quality images and videos.
Challenges in Complex Environments
Flying drones in complex environments such as urban areas and forests presents unique challenges. These include obstacles, signal interference, and unpredictable weather conditions. Careful planning and risk assessment are essential before flying in such environments.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued safe operation.
Post-Flight Checklist

- Power down the drone and controller.
- Inspect the drone for any damage.
- Clean the drone body and propellers.
- Store the battery properly (ideally at a moderate temperature).
- Store the drone in a safe, dry place away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight.
Regular Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting, How to operate a drone
Regular maintenance includes cleaning the drone, inspecting propellers and other components for damage, and checking the battery health. Troubleshooting common issues, such as low battery warnings, GPS signal loss, or motor problems, is essential for safe and efficient operation. Consult your drone’s manual for specific maintenance recommendations.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires a solid grasp of the fundamentals, and a great resource to help you learn is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will equip you with the knowledge to confidently and safely operate your drone, ensuring a positive flying experience.
Remember to always prioritize safety when learning how to operate a drone.
Routine Inspections and Component Replacements
A regular schedule for inspections and component replacements is vital. The frequency of inspections and replacements depends on the drone’s usage and the environment in which it operates. Keep records of maintenance to track component lifespans.
Safe Drone Storage
Store your drone in a safe, dry place, protected from extreme temperatures, moisture, and direct sunlight. Using a protective case can help prevent damage during transport and storage.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to all applicable laws and regulations. These vary by region, so it’s crucial to research your local regulations before flying.
Key Regulations and Laws

- Registration requirements (many countries require drone registration).
- Airspace restrictions (no-fly zones near airports and other sensitive areas).
- Limitations on flight altitude and distance.
- Restrictions on flying at night or in certain weather conditions.
- Privacy regulations (avoiding unauthorized surveillance).
Drone Registration and Permits
Many regions require drone registration before operation. Depending on your intended use, you may also need specific permits or licenses. Check with your local aviation authority for details.
Restrictions on Flight Locations
Flying near airports, crowded areas, and sensitive locations such as power plants or prisons is typically prohibited. Airspace maps and apps can help you identify restricted areas.
Understanding Airspace Restrictions and Obtaining Authorization
Airspace restrictions are in place to ensure safety and security. For flights in controlled airspace, you may need to obtain authorization from the relevant aviation authority. Utilize official airspace maps and follow the procedures for obtaining necessary permissions.
Mastering the art of drone operation opens up a universe of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient data collection. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, and prioritizing safety and legal compliance at every stage, you can confidently explore the world from a unique perspective. Remember that continuous practice and adherence to best practices are key to becoming a skilled and responsible drone pilot.
Safe flying!
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety protocols and legal considerations, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to ensure you’re fully prepared before your first flight.
Ultimately, responsible operation ensures both a safe and enjoyable experience.
Popular Questions: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and automated flight modes. Research models known for their ease of use and robust safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass and GPS?
Calibrate before each flight, especially if you’ve moved locations or experienced any significant impacts. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately engage the Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, try to regain control using basic maneuvers. If still unsuccessful, prioritize safety and let the drone land where it will.
How do I legally fly my drone in a national park?
Check with the specific national park’s regulations; many restrict or prohibit drone flights. Always obtain necessary permits before flying in restricted areas.